Alluxio Data Orchestration Aims To Bring Speed and Agility to Big Data and AI Workloads
Alluxio has updated its data orchestration to simplify and accelerate how firms work with distributed data-intensive workloads. Alluxio 2.0 provides a novel layer of technology to separate compute from storage and automates data ‘tiering’ across on-prem and cloud.
Alluxio has released a major update to its data orchestration platform.
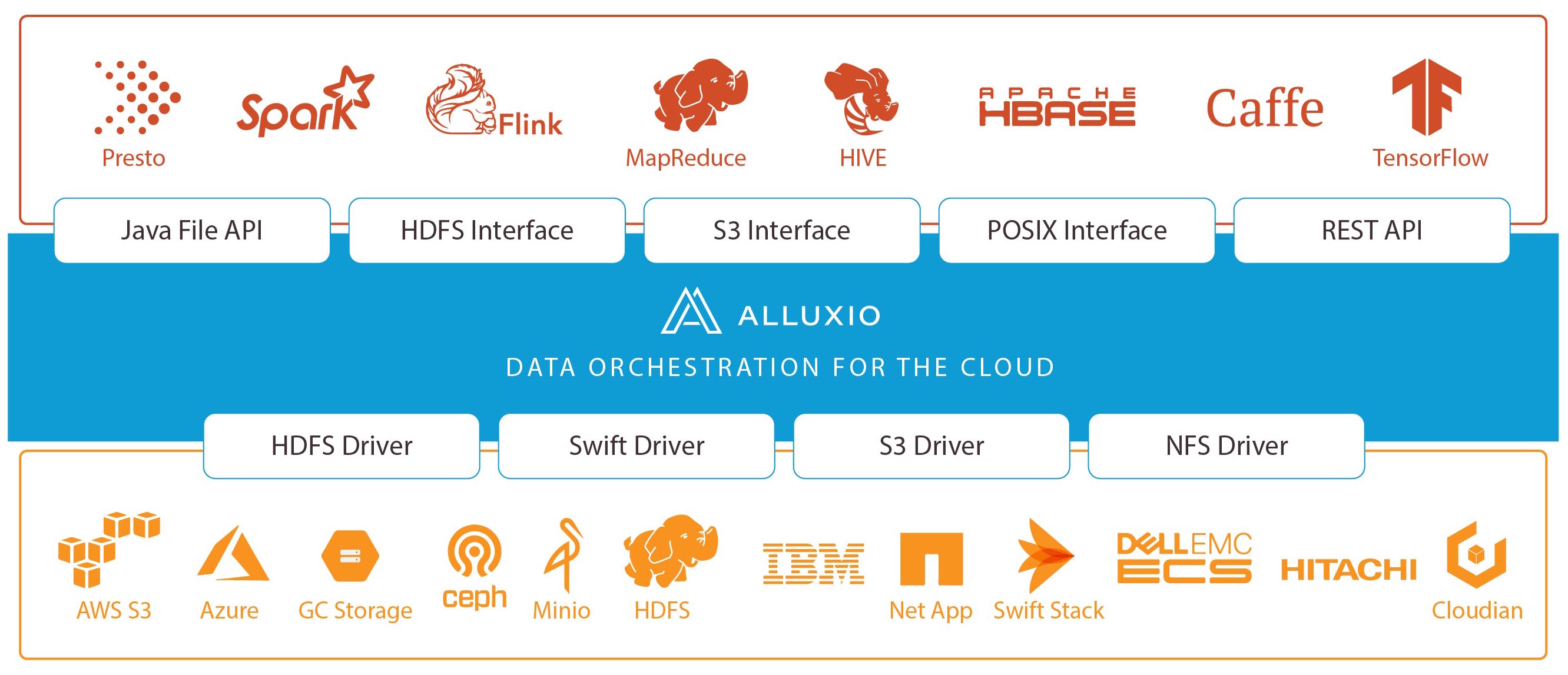
Alluxio 2.0 delivers a platform technology to simplify and accelerate how firms work with distributed data-intensive workloads – across on-prem, cloud and multi-clouds. It does so by delivering a new layer that separate compute from storage.
“A unified data orchestration platform simplifies your data’s cloud journey,” noted Alluxio CEO Steven Mih. Alluxio 2.0’s data orchestration platform offers several crucial capabilities for cloud-centric projects. It includes the ability to:
- abstract data access across storage systems,
- virtualizing all the data and
- presenting that data via standardized APIs (with global namespaces) to data-driven apps.
Alluxio 2.0 unifies dispersed data silos – whether on-premise or running on popular cloud platforms. It also provides data locality, accessibility and elasticity to reduce the complexities associated with orchestrating data for big data and AI/ML workloads.
With the added technology, Alluxio 2.0 lets data engineers automate data movement across multiple storage systems using pre-defined policies.
Alluxio’s core technology was built from the ground up to orchestrate data from different systems and move it closer to different technologies.
“Data platform teams can now reduce storage costs by automatically managing only the most important data in expensive storage systems and moving other data to cheaper storage alternatives,” Mih said, adding, ”It brings speed and agility to big data and AI workloads and reduces costs by eliminating data duplication and enables users to move to newer storage solutions like object stores.”
Alluxio 2.0 Updates for Amazon Web Services
Among its specific support for Amazon cloud users, Alluxio 2.0 also adds AWS Elastic Map Reduce (EMR) service integration.
As users move to cloud services to deploy analytical and AI workloads, AWS EMR (and similar services) are becoming more popular. Alluxio 2.0 can be seamlessly bootstrapped into an AWS EMR cluster, which makes it available as a data layer within AWS EMR for Spark, Presto and Hive frameworks.
“Users now have a high-performance alternative to either cache data from S3 or remote data. Another benefit is that it reduces data copies maintained in EMR,” Alluxio CTO and co-founder Haoyuan Li said.
In an earlier blog post, CTO Li explained more about Alluxio’s vision for cloud-friendly data orchestration.
“In order to fundamentally solve the data access challenges, the world needs a new layer – a data orchestration platform – between computation frameworks and storage systems. A data orchestration platform abstracts data access across storage systems, virtualizes all the data, and presents the data via standardized APIs with global namespace to data-driven applications.
‘Data Orchestration’ Drives Benefits Similar to ‘Container Orchestration’
Li also likened Alluxio’s vision for data orchestration to another popular cloud architecture.
“Like container orchestration enables containers to run in any environment agnostic to the hardware that is running the application, data orchestration enables applications to be compute-, storage- and cloud-agnostic.”
In a separate blog post, Alluxio vice president Dipti Borkar shared more details about the benefits of data orchestration, especially for cloud and multi-cloud projects:
We firmly believe that just like compute and containers need orchestration by something like Kubernetes, data that’s increasingly siloed and the working set for compute workloads also needs orchestration – data orchestration. Bringing data closer to compute to accelerate jobs, making data more accessible via different APIs and being able to abstract data apps from where the data is stored, are all core concepts we have built on.
In addition to fine-grained policies at the file level, users can also configure policies at any directory and folder level to streamline access of data as well as performance of workloads. These include defining behaviors for individual datasets on various core functions like writing data or syncing data with storage systems.
Borkar went on to describe how Alluxio’s combination of dynamic orchestration and policy-driven data management enables enterprises to easily achieve a ‘tiered’ set of data that can supercharge value.
[A]s data is created -- and ‘hot,’ ‘warm,’ and ‘cold’ data is managed -- Alluxio can automate tiering of data across any number of storage systems across on-premises and across all clouds.
Such benefits jump out especially for companies looking to bring AI/ML into their data-driven projects (apps, analytics and more).
“Data-driven analytics that were once run over many hours, now need to be done in seconds,” Mih noted. “AI/ML models need to be trained against larger-and-larger datasets. This all points to the necessity of a data tier which orchestrates the movement and policy-driven access of a companies' data, wherever it may be stored. Alluxio abstracts the storage and enables a self-service culture within today's data-driven company."
The latest updates in Alluxio 2.0 reflect the company’s commitment to a cloud-native, open source approach to enabling applications to be compute, storage and cloud agnostic, he added.
Alluxio 2.0 includes other capabilities worth noting, including:
Alluxio Data Service. This is a distributed clustered service for crucial data operations such as replication, persistence, to enable high performance and super-scale.
Cross Cloud Storage Efficient Data Movement via Data Service. This allows for highly efficient data movement, including across cloud stores like AWS S3 and Google GCS, making expensive operations on object storage seamless to the compute framework.
High Availability with Embedded Journal. This delivers a fault tolerance and high availability mode for file and object metadata. The “embedded journal” feature uses the RAFT consensus algorithm and is independent of any other external storage systems. It is particularly useful for abstracting object storage.
Integration with External Data Sources Over REST. This lets users bring in data even from web-based data sources to aggregate in Alluxio and be pulled in as needed based on the query or model run.
Alluxio 2.0 is available now in a Community (open source) and Enterprise Edition.









